- Spec ID:
ausdigital-bill/1
- Editor:
- Contributors:
- Introduction
- Goals
- Status
- Glossary
- Licence
- Change Process
- Language
- Billing Process
- State Lifecycle
- UBL Document Identifiers
- CustomizationID
- Invoice Document Profiles
- Application Response Document Profile for AusDigital BILL
- Service Registry Bindings
- Document Identifier
- Process Identifier
- Transport Layer Bindings
- Conversations
- Attachments
- UBL Syntax 1.0 Billing Document Specifications
- Invoice Document
- Response Document
- UBL Syntax 2.0 Billing Document Specifications
- Invoice Document
- Response Document
- Validation Rules
- Validation Rules - Common
- Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-invoice”
- Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-rcti”
- Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-taxreceipt”
- Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-adjustment”
- Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”creditnote”
- Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-debitnote-v1”
- Related Material
Introduction
This document describes the AusDigital Billing Semantics (BILL) 1.0 Specification. It is not yet a proposed standard, only an early draft for discussion.
Goals
- To provide a clear and unambiguous specification for the exchange of invoices between any two business systems.
- To ensure that there is sufficient business value to both the buyer (accounts payable automation) and the supplier (accounts receivable automation) so that there is a compelling buisness case for implementation.
These are achieved by:
- A strong focus on the invoice state lifecycle and the interactions that change the state of an invoice - particularly the response documents from buyer to seller.
- Coverage of all invoice types (invoice, debit note, credit note, adjustment invoice, RCTI, tax receipt)
- A clear mapping from process context to document properties and business rules that are relevant to the process.
Status
This spec is an early draft for consultation.
This specification aims to support the Australian Digital Business Council eInvoicing initiative, and is under active development at https://github.com/ausdigital/ausdigital-bill.
Comments and feedback are encouraged and welcome. Pull requests with improvements are welcome too.
Glossary
| Phrase | Definition |
|---|---|
| ausdigital-bill/1 | This specification. |
| ausdigital-code/1 | Version 1 of the AusDigital Code Lists Management (CODE) specification. |
| ausdigital-syn/1 | Version 1 of the AusDigital UBL Syntax(SYN) specification. |
| ausdigital-syn/2 | Version 2 of the AusDigital UBL Syntax(SYN) specification. |
This service depends on - TBA.
The TBA specification depends on this document. Note, TBA.
Licence
Copyright (c) 2016 the Editor and Contributors. All rights reserved.
This Specification is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This Specification is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program; if not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
Change Process
This document is governed by the 2/COSS (COSS).
Language
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119.
Billing Process
The Ausdigital billing process is based on the internaltional UBL billing process and uses the UBL2.1 Invoice and document response schema.
State Lifecycle
The diagram shows the allowed set of states for an invoice as understood by both parties in the collaborative process. Every transition from one state to another is triggered by the exchange of a business message - which could be either an invoice (one of six profiles) or a response document (with one of four response codes).
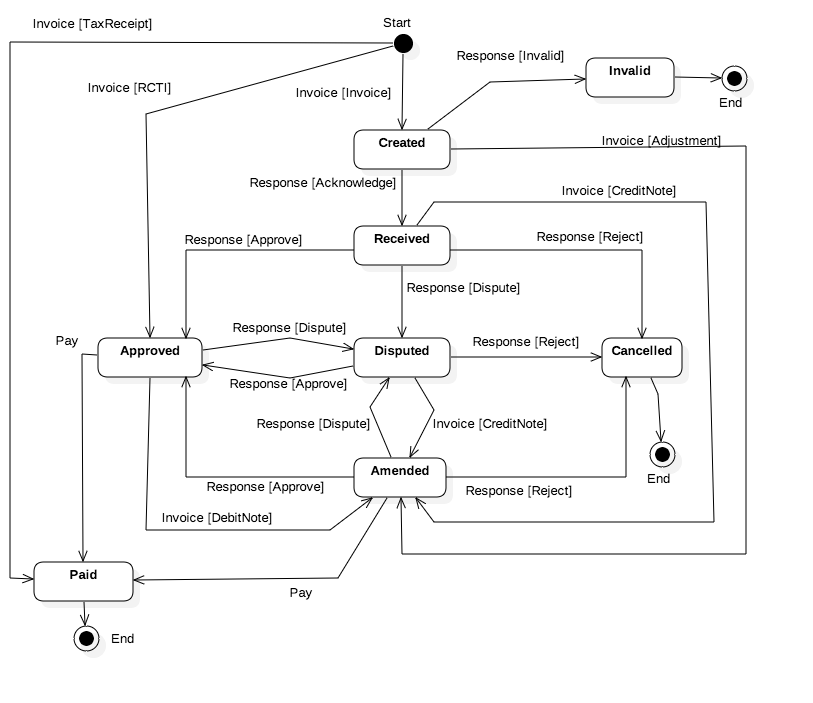
- The TaxReceipt has the simplest lifecycle because it is just a record of a previous payment and so there is only a single invoice (
"ProfileID":"bill-taxreceipt-v1") sent from seller to buyer and the state is “paid”. No document response needed. - The receipt of an RCTI (
"ProfileID":"bill-rcti-v1") by a seller from a buyer takes the state directly to “approved” because this is a payer initiated transaction. However the payer may subsequently send an invoice ("ProfileID":"bill-debitnote-v1") to make an adjustment to the rcti prior to eventual payment is accordance with payment terms. - The standard invoice (
"ProfileID":"bill-invoice-v1") that is a demand for future payment from seller to buyer is the most complex lifecycle because there can be :- various response documents indicating buyer processing status (acknowledged, approved, disputed, rejected)
- a re-issue of the invoice with changes (
"ProfileID":"bill-adjustment-v1") from seller to buyer - usually in response to a disputed status. - an issue of a credit note against an existing invoice (
"ProfileID":"bill-creditnote-v1") - also usually in response to a disputed status. - an outright rejection of the invoice by the buyer which leads to a cancelled end-state.
- The “success” end state in all cases is “paid” - indicated by the receipt of a payment record from a bank reconciliation file (outside of the scope of this specification).
- In some cases a received invoice may be invalid (ie unreadable or does not comply with mandatory business rules). In that case, the invoice is rejected and the state becomes “invalid”. The sender must fix and start again.
UBL Document Identifiers
CustomizationID
UBL CustomizationID is used to identify the authority that is responsible for the localisation of the UBL for a specific jusridiction or industry context.
For all UBL documents exchanged in accordance with this BILL specification, the customizationID is always “ausdigital.org” ("CustomizationID":"ausdigital.org").
Invoice Document Profiles
The same UBL 2.1 Invoice document is used in six different ausdigital process contexts, indicated using the UBL ProfileID.
In all cases, the Schema reference is “urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:Invoice-2”
- For XML syntax, this is the xmlns namesapce reference.
- for JSON syntax, this value is carried in the “_D” element.
The Allowed values for the UBL document “ProfileID” element are:
- Standard invoice from seller to buyer (
"ProfileID":"bill-invoice-v1") - Updated standard invoice from seller to buyer that replaces a pervious invoice of the same ID (
"ProfileID":"bill-adjustment-v1") - Recipient created tax invoice from buyer to seller (
"ProfileID":"bill-rcti-v1") - Tax receipt sent from seller to buyer after payment has been made - usually for POS or online purchases (
"ProfileID":"bill-taxreceipt-v1") - Credit note sent from seller to buyer that references an earlier standard invoice (
"ProfileID":"bill-creditnote-v1") - Debit note sent from buyer to seller that references an earlier RCTI (
"ProfileID":"bill-debitnote-v1")
The detailed business validation rules for each invoice profile are defined in Validation Rules.
Application Response Document Profile for AusDigital BILL
The UBL Application response document is used in many different process contexts. In all cases, the Schema reference is “urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:ApplicationResponse-2”
When used to indicate invoice status information in the BILL lifecycle, the applicationResponse document will always carry the the same profileID:
- Application response to AusDigital BILL Invoice (
"ProfileID":"bill-response-v1")
A UBL document response provides a means for the receiver party to update the sender on the processing state of the invoice. The set of valid document response codes is defined by the state lifecyle. The allowed values are:
"responseCode":"UT"- invalid, returned by the recipient ledger if the invoice document does not validate. Error details should be sent in the “description” element."responseCode":"AB"- acknowledged, confirms receipt of the invoice (but does not imply approval to pay)."responseCode":"AP"- approved, means that the payer has approved the invoice for (future) payment in accordance with payment terms."responseCode":"DI"- disputed, means that the payer has not accepted the invoice and will dispute some or all of the invoice."responseCode":"RE"- rejected, means that the payer has rejected the entire invoice and will not be paying.
Service Registry Bindings
This section describes how the Digital Capability Publisher Service Metadata structure should be populated in order to describe a participant’s support for the BILL specification.
Document Identifier
“DocumentIdentifier” MUST follow the global SMP and UBL specifications for a UBL invoice to indicate simply that this is a UBL 2 invoice document.. Namely
- “scheme”=”bdx-docid-qns” and
- “value”=”urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:Invoice-2”
Process Identifier
The DCP “ProcessIdentifier” identifies the process context and so MUST map directly to the UBL ProfileID:
- “Scheme” = “digitalbusinesscouncil.com.au” and
- “value” = the same as the UBL “ProfileID” value - “bill-rcti-v1”
Transport Layer Bindings
The invoice document is exchanged in accordance with the TAP protocol. This paragraph describes the binding between the business seamntic layer and the TAP messaging protocol layer.
Conversations
As a buyer and seller ledger, I need a way to connect business semantics to message semantics with a unique and durable key such as a so that I can share it with interested third parties and limit what they can see to just the transaction I want to share. This requirement is met as folows:
- The invoice state lifecycle defines the scope of one e-invoice “conversation”
- There MUST be a unique identifier for each “conversation” and it MUST be placed into the TAP header “reference” field
- The identifier MUST created by the initiator of the conversation
- The identifier MAY be a business level identifier such as in invoice number so long as it is unique between buyer and seller (ie no other conversations with the same identifier can exist).
- The identifier MUST be maintained by the participating (buyer and seller) ledgers as the durable link between the business layer and messaging layer.
Attachments
In many cases, the seller may wish to send additional documents together with the UBL invoice. Typical examples are:
- a human readable PDF version of the invoice, or
- a timesheet that supports the charges in the invoice, or
- a metering breakdown that supports a utility invoice.
These are sent as separate “attachment” messages at any time after the related semantic document. The attachment message is handled like any other message in the e-invoicing exchange except that it:
- MUST include the TAP header “attachedTo” property which MUST contain the same value as the “hash” property of the referenced message.
UBL Syntax 1.0 Billing Document Specifications
The billing process is supported by the invoice document (six variants) and the response document (four status codes) as described in the billing process model. This section specifies the required invoice and response document models.
Invoice Document
Is defined by the DBC CoreInvoice XML Schema library.
Response Document
Is defined by the DBC Document Response XML Schema library.
The response document is a generic structure for all UBL document responses. The generic response becomes a meaningful invoice response via the correct population of two key fields:
- “profileID” which MUST be one of the 6 invoice profiles define in the billing process
- “statusReasonCode” which MUST contain one of the 4 values defined in the invoice response codes
UBL Syntax 2.0 Billing Document Specifications
The billing process is supported by the invoice document (six variants) and the response document (four status codes) as described in the billing process model. This page specifies the required invoice and response document models.
Invoice Document
Is defined by the Invoice Schema which is a simple single root JSON Schema that is a semantically equivalent representation of the DBC CoreInvoice XML Schema library.
Response Document
Is defined by the Response Schema which is a simple single root JSON Schema that is a semantically equivalent representation of the DBC Document Response XML Schema library.
The response document is a generic structure for all UBL document responses. The generic response becomes a meaningful invoice response via the correct population of two key fields:
- “profileID” which MUST be one of the 6 invoice profiles define in the invoice document profiles
- “statusReasonCode” which MUST contain one of the 4 values defined in the invoice response codes
Validation Rules
Validation rules from the ADBC eInvoicing Semantic Model are re-stated here but are broken down according to the invoice document usage context as identified by the ProfielID element.
Validation Rules - Common
| Rule | Mandatory | Optional | Extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| An Invoice of more than $82.50 (including GST) to a GST-registered Buyer MUST be a Tax Invoice. | X | ||
| An Invoice must contain a Document Type Code | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST contain the Supplier’s Business Name or the ABN of the Supplier. | X | ||
| An Invoice with a Total Amount greater than $1000 MUST have either the Buyer’s Business Name or the ABN of the Buyer. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY contain the ABN plus a GST branch number for Suppliers with GST branches registered with the ATO. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST contain an Invoice Issue Date. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MUST have a Description. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY contain a Description of Properties of Invoiced Items. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY contain an Invoiced Quantity. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MUST contain the Invoice Line Extension Amount (Net Price multiplied by Invoiced Quantity) (excluding GST) for the Items sold. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST contain the sum total of all Invoice Line Extension Amounts. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MUST contain the GST Amount for the Items sold or indicate the extent to which Items are taxable. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MUST contain the Amount Payable (Invoice Line Extension Amount plus GST Amount) for the Items sold. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY contain a GST Amount of zero. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY specify a GST Category. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST contain the Invoice level Tax Amount exclusive of GST. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST contain the Invoice level GST Total Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have an Invoice Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have a Supplier Business Name. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have a valid Document Type Code. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have an Issue Date. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have a Delivery Date. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Invoice Period. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Invoice Period Start Date. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Invoice Period End Date. | X | ||
| An Invoice End Period Date MUST be later or equal to an Invoice Period Start Date. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have a Sales Order Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have a Purchase Order Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have a Contact Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Electronic Address. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have at least one Invoice Line. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Item MAY have a Suppliers Item Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Item MUST have a Description. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Quantity. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Net Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Dispatch Advice Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Receipt Advice Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a delivery Address. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Item MAY have a Country of Origin. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have one or more Document References. | X | ||
| The Invoice Level Net Amount MUST be equal to the sum of Invoice Line Net Amounts. | X | ||
| The Invoice Level Allowance Amount MUST be equal to the sum of Invoice Line Allowances plus any Invoice Level Allowances. | X | ||
| The Invoice Level Charge Amount MUST be equal to the sum of Invoice Line Charges plus any Invoice Level Charges. | X | ||
| The Invoice Level Net Amount MUST be equal to the Invoice Level Gross Amount - Invoice Level Allowance Amount + Invoice Level Charge Amount. | X | ||
| The Invoice Level GST Amount MUST be equal to the sum of Invoice Line GST Amounts. | X | ||
| The Invoice Level Total Amount MUST be equal to the Invoice Level Net Amount + the Invoice Level Tax Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Amount Payable. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have an Invoice Level Total Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Invoice Level Net Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have a Related Invoice Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Amount Payable. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have one or more Document References. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Total Amount MUST be greater than 0. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Net Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Extended Amount after all allowances and charges MUST NOT be negative. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Price MUST be 0 or more. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Item MUST have a Net Price. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Quantity. | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have an Allowance Rate and Base Amount at Invoice Level. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Allowance MUST be greater than 0. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Allowance MAY have a GST Category. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Allowance Reason Description MUST match the Invoice Level Allowance Reason Code (if any). | X | ||
| An Invoice MAY have a Charge Rate and Base Amount at Invoice Level. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Charge MUST be greater than 0. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Charge MAY have a GST Category. | X | ||
| An Invoice Level Charge Reason Description MUST match the Invoice Level Charge Reason Code (if any). | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have an Allowance Rate and Base Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Allowance MUST be greater than 0. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Allowance MUST have an Allowance Reason Description. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Allowance Reason Description MUST match the Invoice Line Allowance Reason Code (if any). | X | ||
| An Invoice Line MAY have a Charge Rate and Base Amount. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Charge MUST be greater than 0. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Charge MUST have a Charge Reason Description. | X | ||
| An Invoice Line Charge Reason Description MUST match the Invoice Line Charge Reason Code (if any). | X | ||
| A Payment Means MUST have a valid Payment Means Type Code. | X | ||
| A Payment Means Financial Institution Account Identifier MUST have Financial Institution Identifier. | X | ||
| A Payment Means for a card payment MUST state the last 4 to 6 digits of the Financial Institution Account Identifier. | X | ||
| An Invoice MUST have a Payee Business Name if Payee Business Name is not the same as the Suppliers Business Name. | X |
Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-invoice”
| Rule | Mandatory | Optional | Extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Tax Invoice for goods or services that do not all include GST (mixed supplies) shall indicate which goods or services do not include GST. | X |
Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-rcti”
| Rule | Mandatory | Optional | Extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Recipient Created Tax Invoice MUST contain either the Business Name or the ABN of the Buyer. | X | ||
| A Recipient Created Tax Invoice MUST contain the Payee Name if GST is payable. | X | ||
| A Recipient Created Tax Invoice MAY contain the following statement: “The recipient and the supplier declare that this agreement applies to supplies to which this tax invoice relates. The recipient can issue tax invoices in respect of these supplies. The supplier will not issue tax invoices in respect of these supplies. The supplier acknowledges that it is registered for GST and that it will notify the recipient if it ceases to be registered. The recipient acknowledges that it is registered for GST and that it will notify the supplier if it ceases to be registered for GST. Acceptance of this RCTI constitutes acceptance of the terms of this written agreement. Both parties to this supply agree that they are parties to an RCTI agreement. The supplier agrees to notify the recipient if the supplier does not wish to accept the proposed agreement within 21 days of receiving this document.” | X |
Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-taxreceipt”
tbd
Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-adjustment”
| Rule | Mandatory | Optional | Extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| An Invoice MUST contain a Document Type Code indicating it is an adjustment document. | X |
Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”creditnote”
| Rule | Mandatory | Optional | Extension |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Credit Note MAY have a Related Invoice Identifier. | X | ||
| A Credit Note MAY have a Total Amount. | X | ||
| A Credit Note MAY have a Buyer Accounting Reference. | X | ||
| The Credit Note Total Amount MUST be greater than 0. | X | ||
| A Credit Note Line MAY have a Net Amount. | X | ||
| The Credit Note Line Net Price MUST NOT be negative. | X | ||
| A Payment Means Type Code for a Credit MUST have a Financial Institution Account Identifier. | X |
Validation Rules - “ProfileID”:”bill-debitnote-v1”
tbd
Related Material
- ADBC eInvoicing Semantic Model (v1.0, available here), which provides background to the AusDigital community process.
- GitHub issues for collaborating on the development of the BILL.
- A reference BILL service (for testing and development purposes).
- Free, Open-Source Software BILL implementation.
- An automated DCL test suite.
